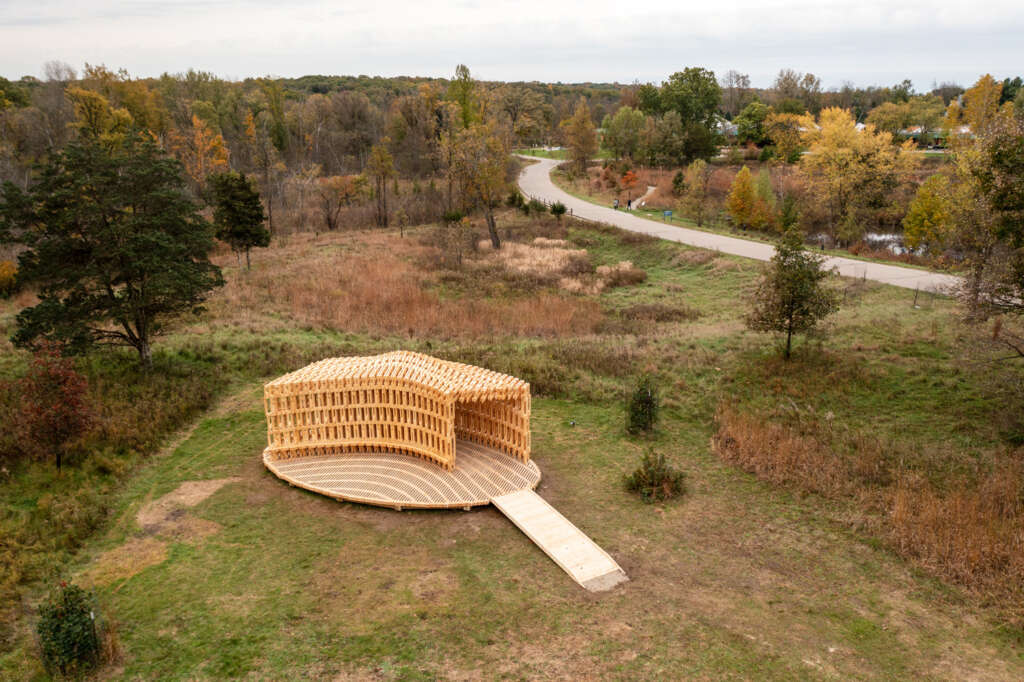

Robotically Fabricated Structure (RFS)
Designer: ADR Laboratory, Taubman College of Architecture and Urban Planning, University of Michigan
Location: Matthaei Botanical Gardens, Ann Arbor, Michigan
Type: Pavilion
Year: 2022
Photographs: Arash Adel, Bob Berg, Daniel Ruan, Matthew Weyhmiller, Mehdi Shirvani, Jacob Cofer
The following description is courtesy of the architects. RFS is a robotically fabricated timber pavilion that explores responsible and precise methods contributing to sustainable and low-carbon construction outlooks. This structure is designed with the help of custom algorithms developed specifically for this project and built through state-of-the-art human-robot collaborative construction. RFS employs bespoke prefabricated timber sub-assemblies manufactured from regionally sourced short 2×4 dimensional lumber and utilizes industrial robotic arms to process and assemble elements into intricately layered modules. After fabrication, modules are transported to the site, where human workers move each sub-assembly into place and attach them together to form the pavilion.
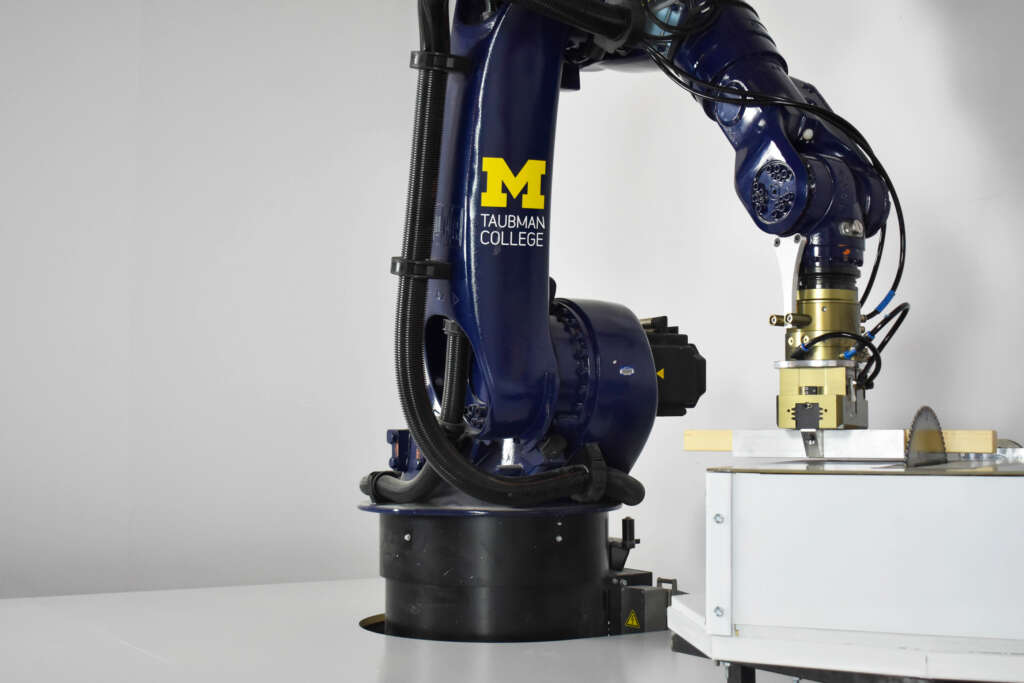
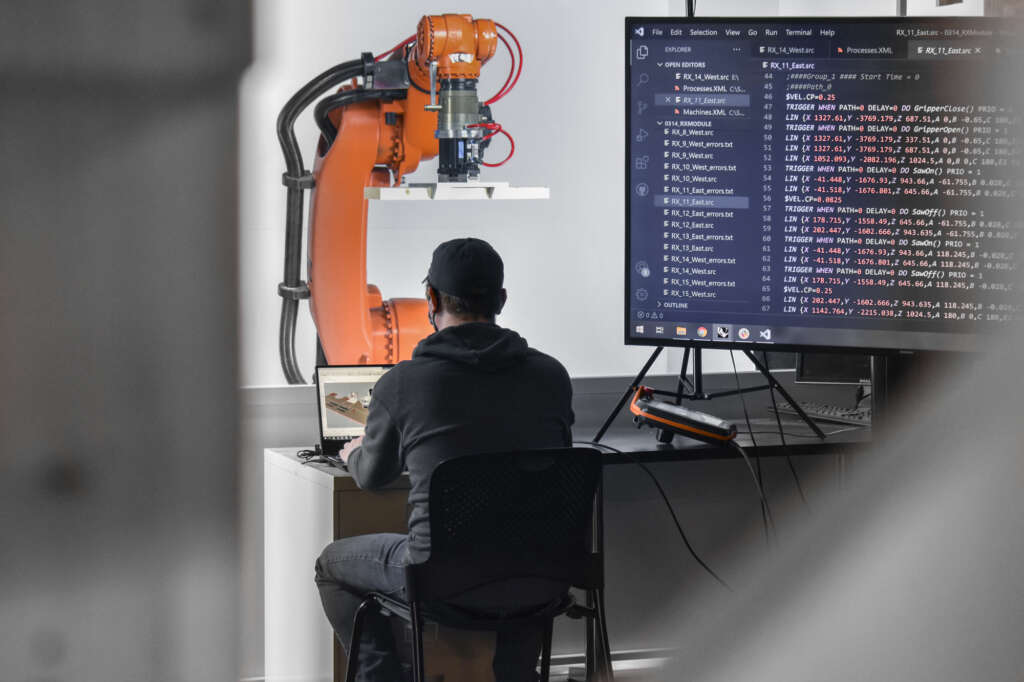
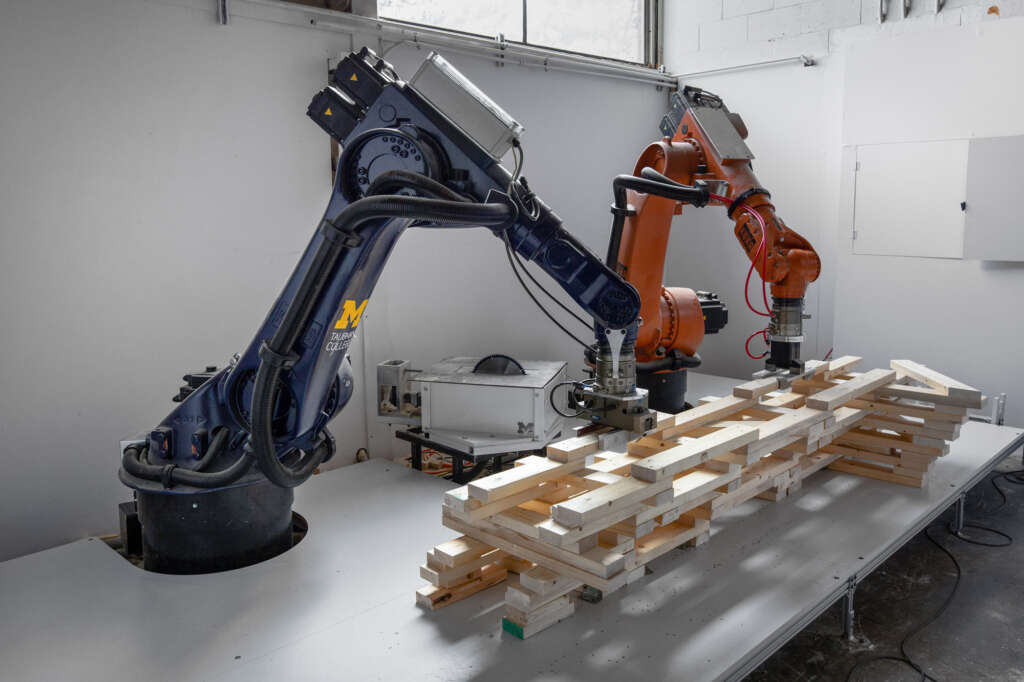
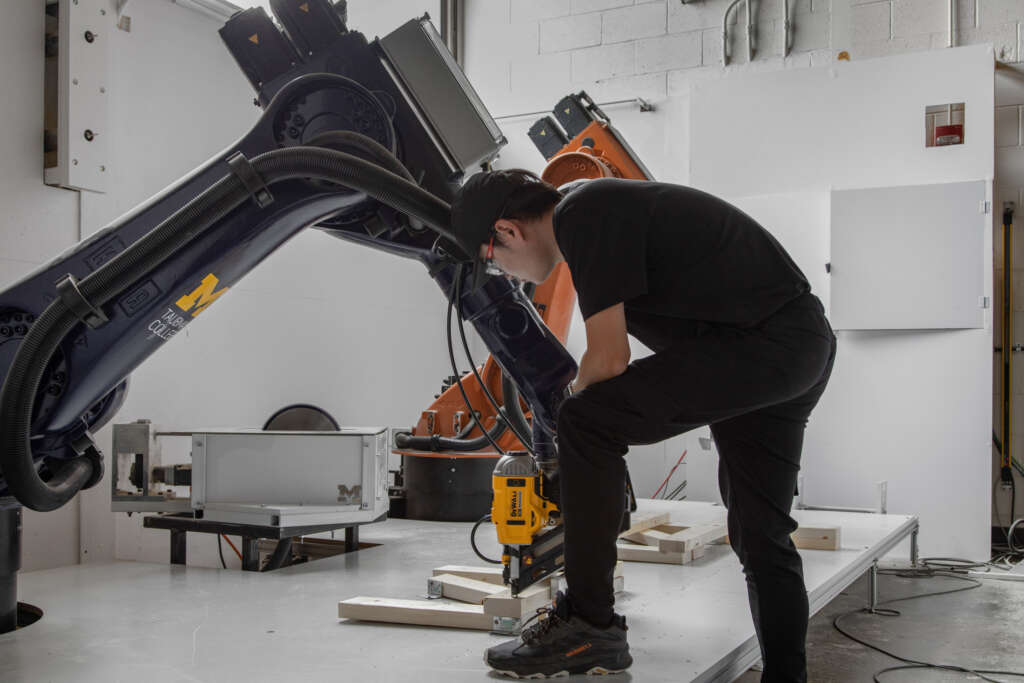
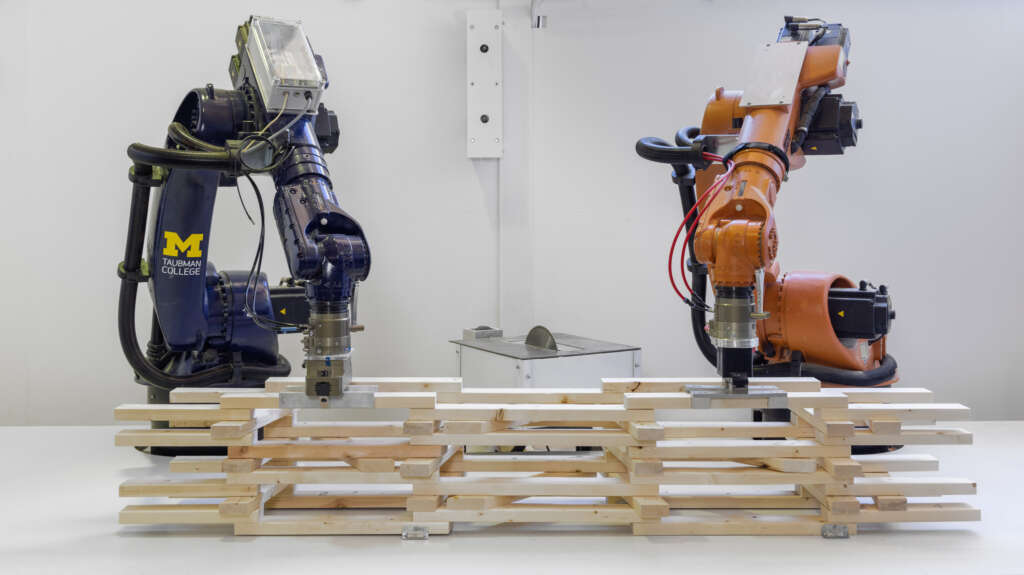




The coupling of custom algorithms and robotic fabrication enables the feasible realization of bespoke building components that are otherwise difficult or costly to achieve through conventional means and methods, with minimal construction waste. Moreover, short elements enable the use of indigenous trees that cannot easily produce full-length building elements (typically eight-foot dimensional lumber), construction and manufacturing off-cuts, and lumber elements reclaimed from the deconstruction of buildings, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable practice. The integrated digital design and construction process for RFS is a novel approach to reconsidering issues of material use, labor, and the environment to create intelligent and resourceful architecture with striking expressive qualities.
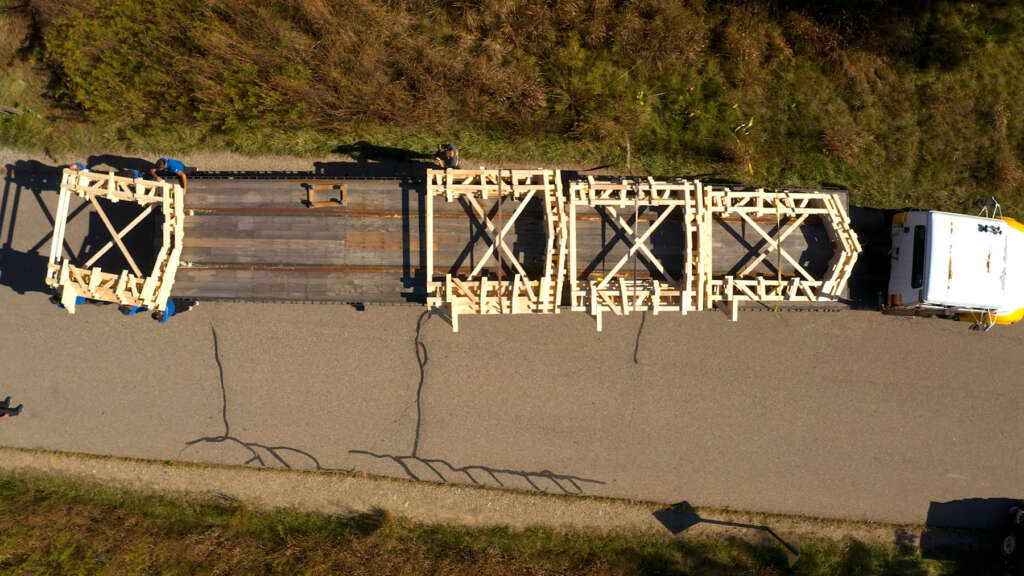
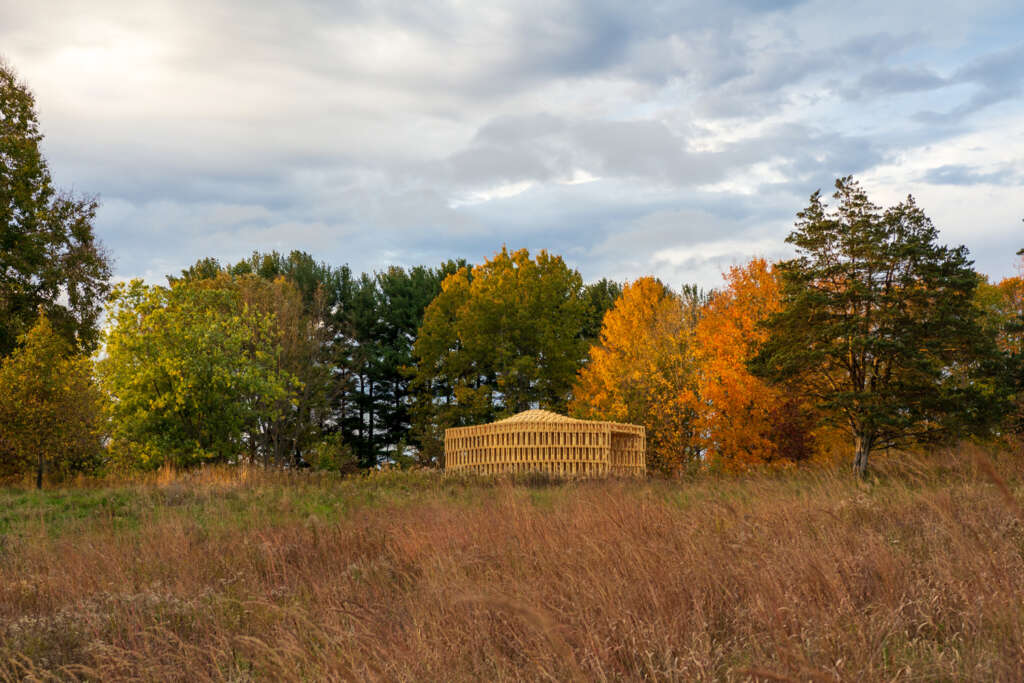
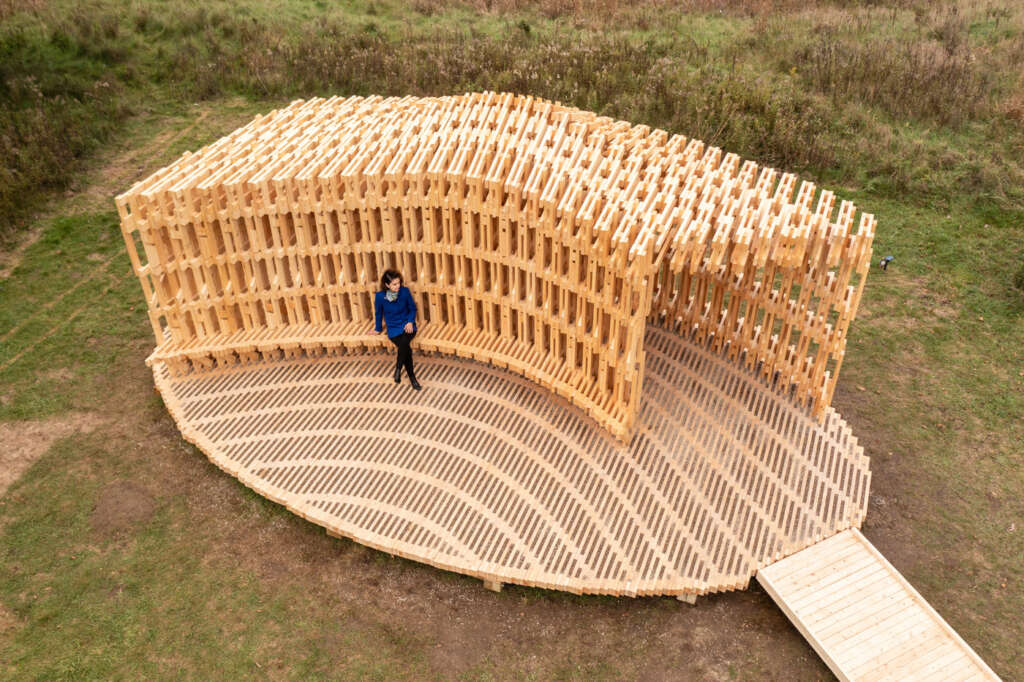
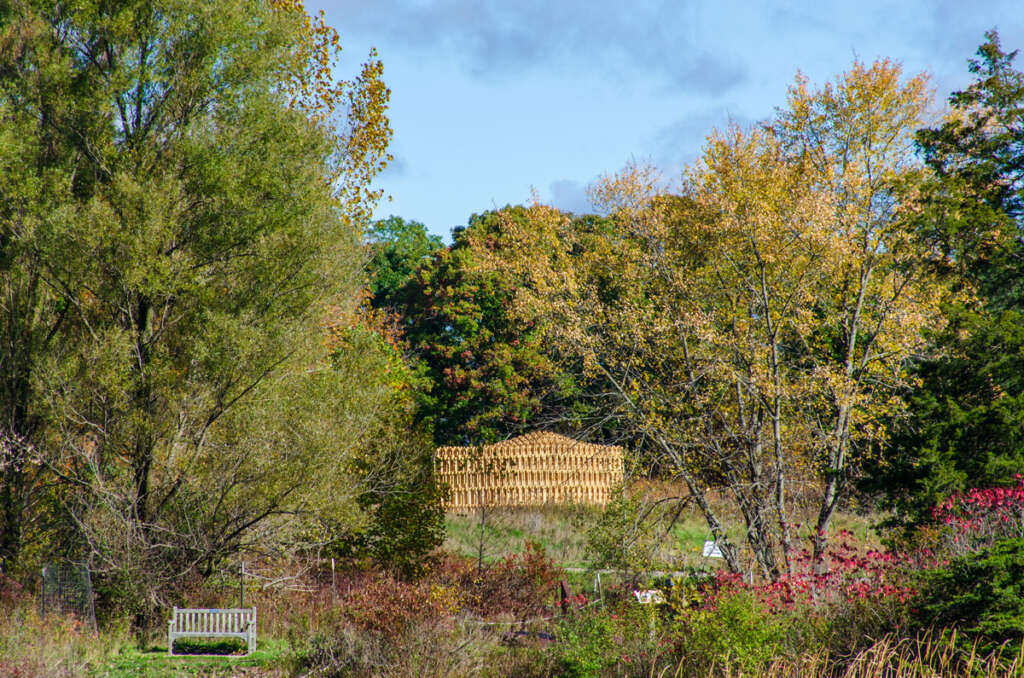




RFS is situated in the Matthaei Botanical Gardens in Ann Arbor, Michigan; it is designed for public engagement, acting as a defined gathering point located within the framework of a public conservatory while still maintaining an open-air condition. Formal configurations of the pavilion were influenced by views to and from the site, approach, and traffic flow, ultimately resulting in a curved, porous structure visible from the park road. The walls and ceiling feature intricately layered patterns of timber that allow for airflow, striking shadows, and optical effects. RFS was left minimally treated to reduce the environmental impact on the surrounding area and produce a long-lasting but impermanent structure. The pavilion includes an enclosed walkway that offers opportunities for exhibitions and intimate conversations, an exterior seating area, and a raised platform that creates an opportunity for small public events and performances.
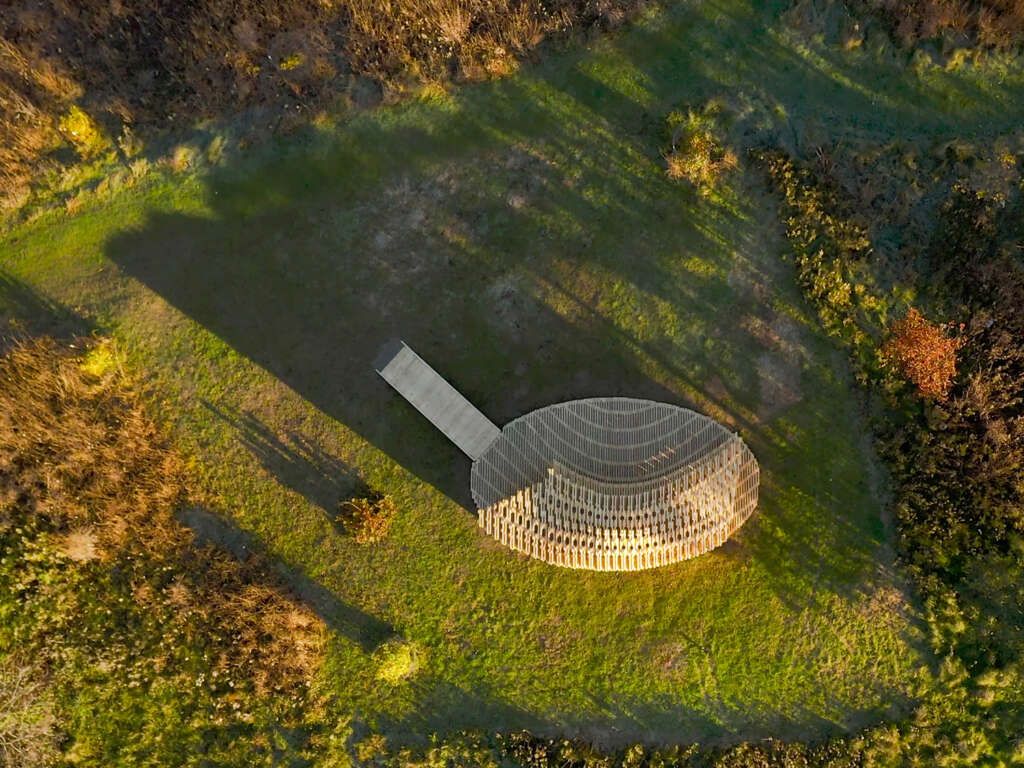
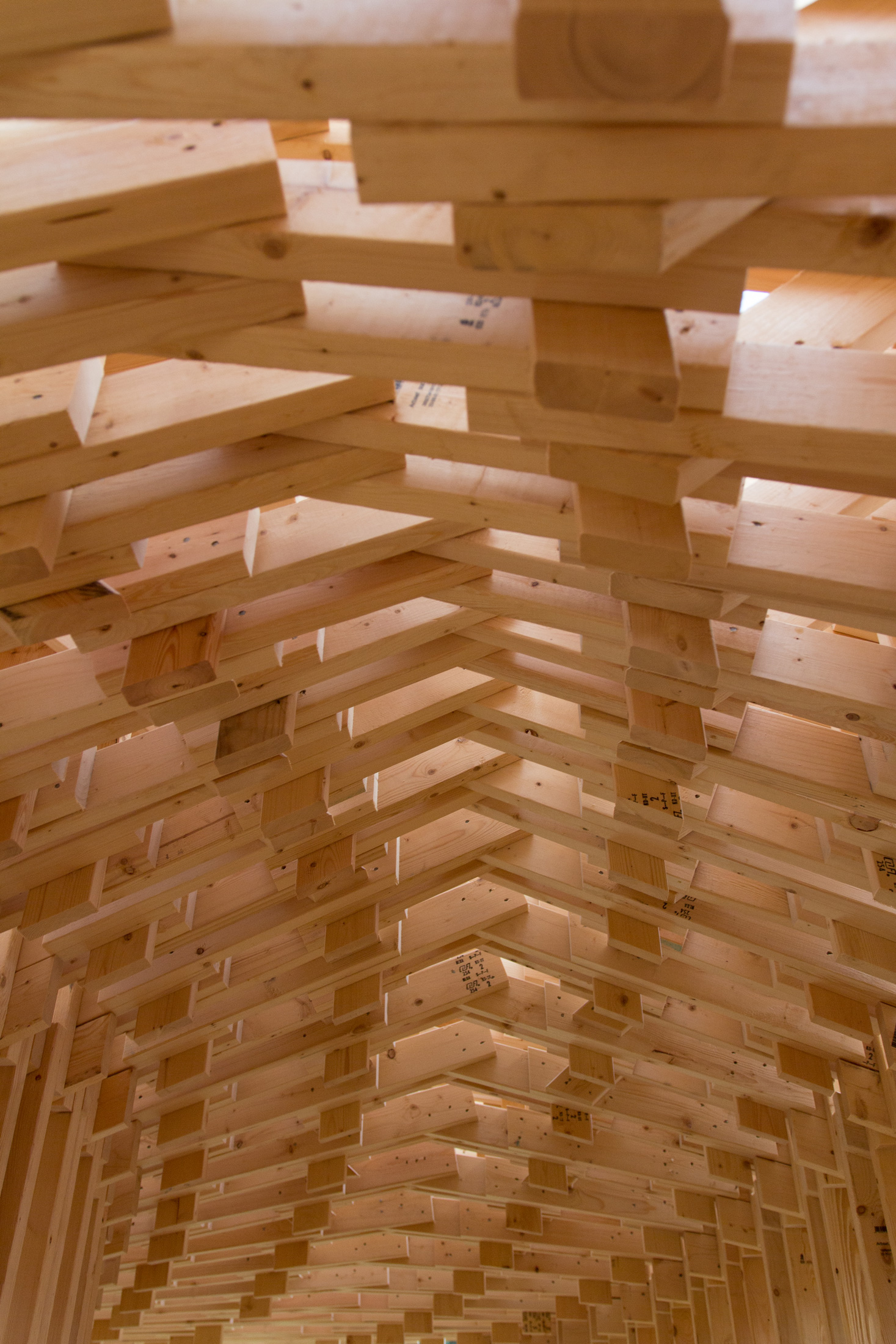
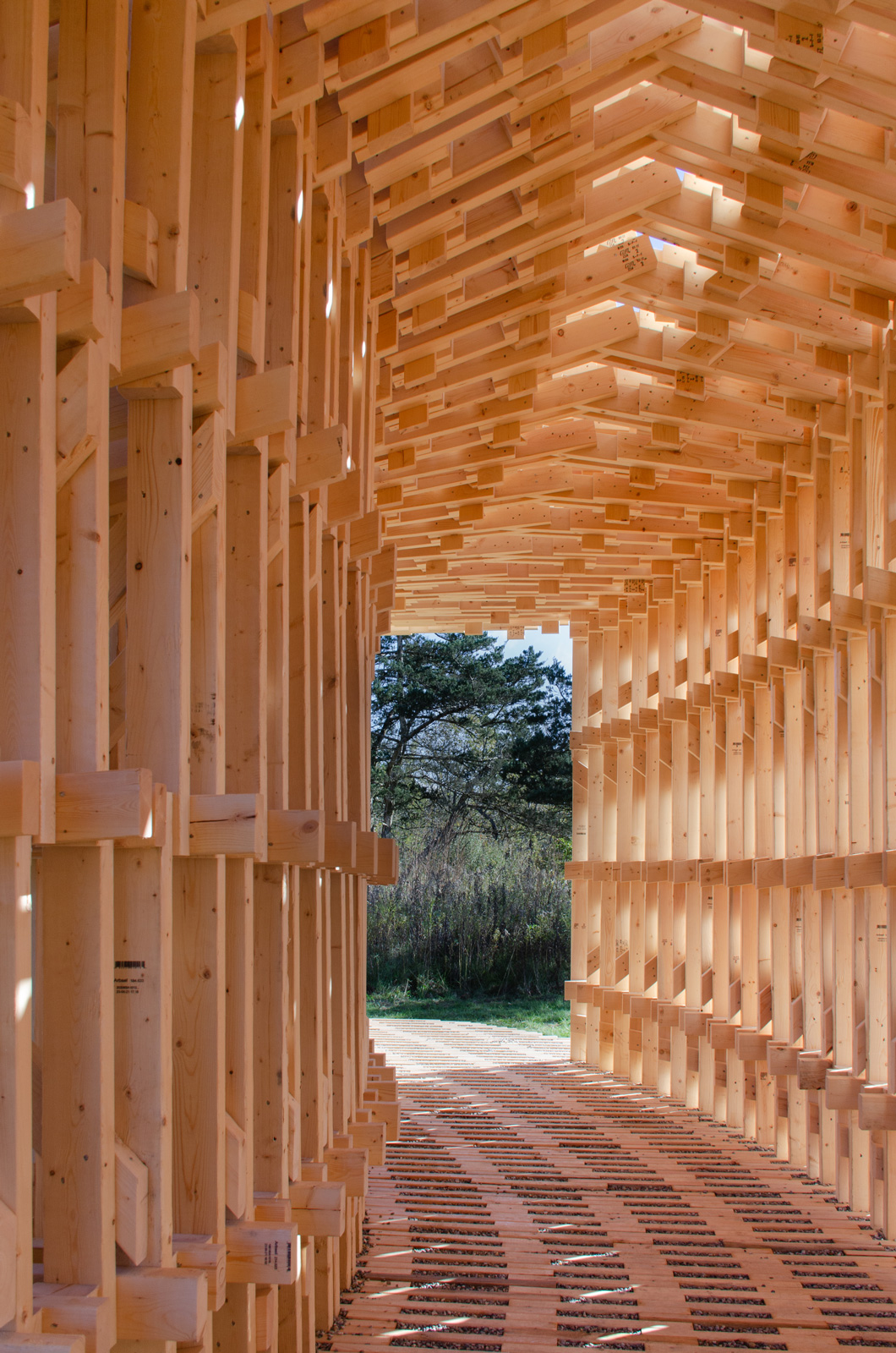
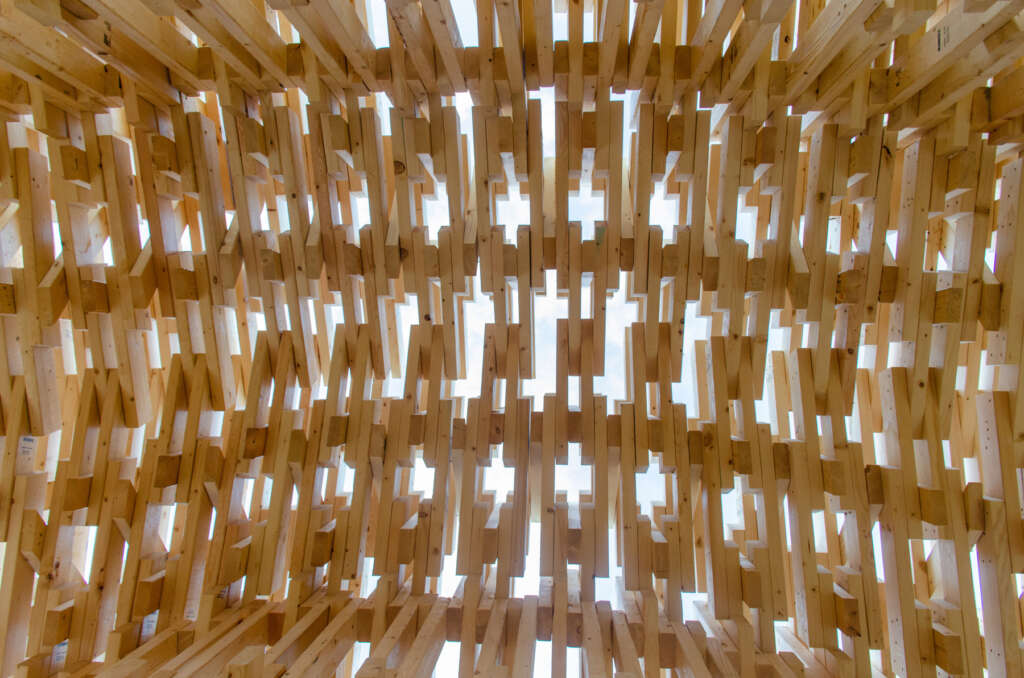
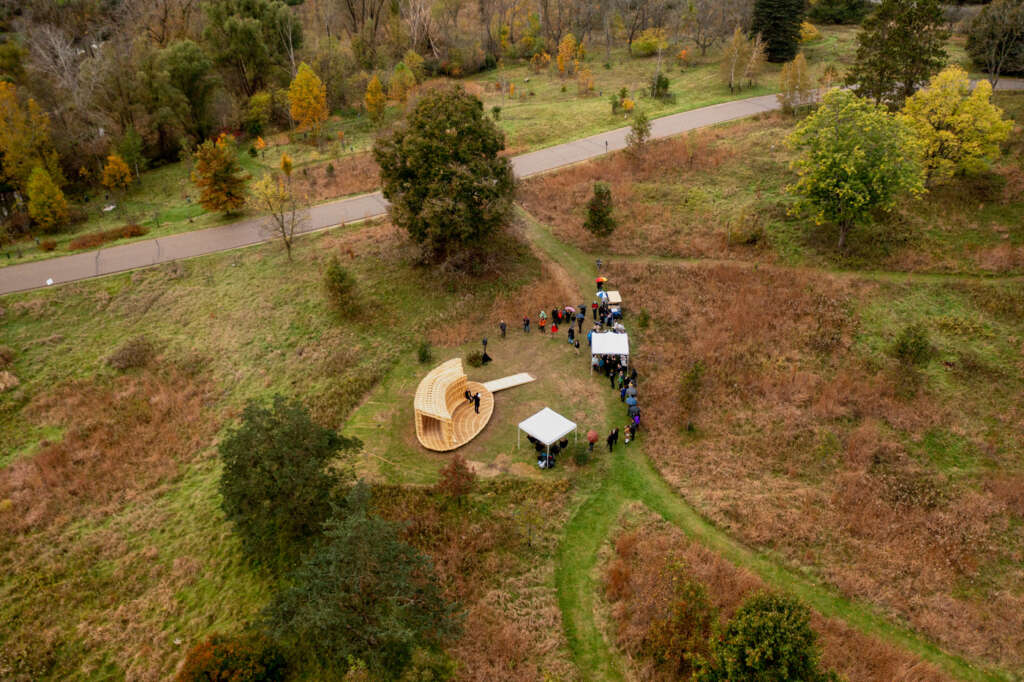





Completing RFS elevated the ongoing research in human-robot collaborative construction beyond the laboratory to the scale and complexity of complete building systems. This case-study project is intended to provoke conversations about appropriate uses of automation in construction and the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) community’s shifting responsibility to find creative solutions to construction inefficiencies and the omnipresent threat of climate change.
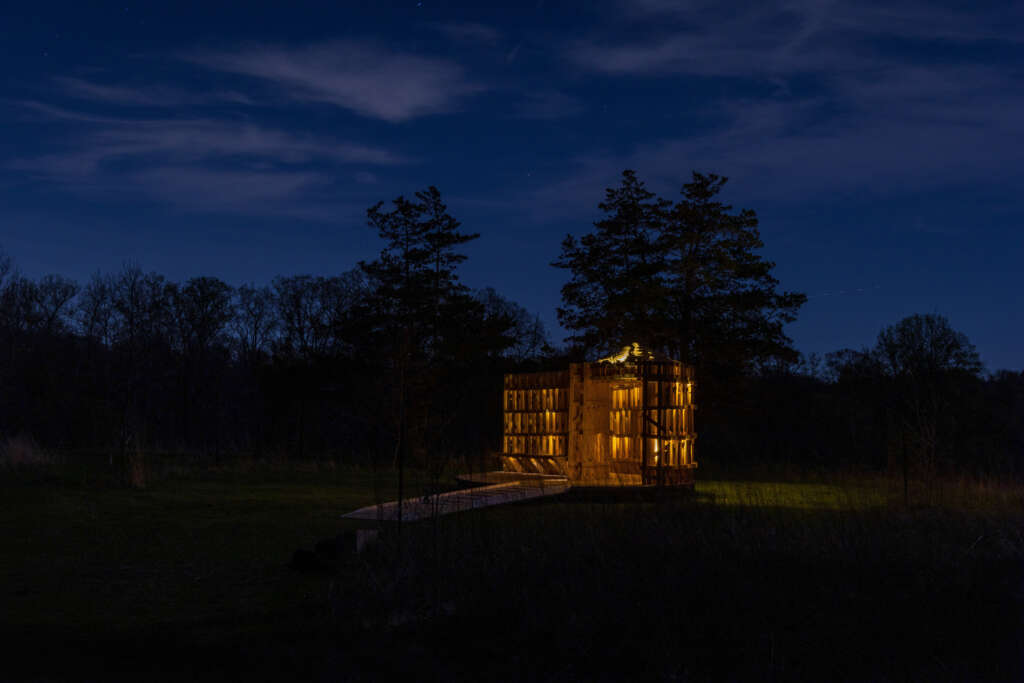
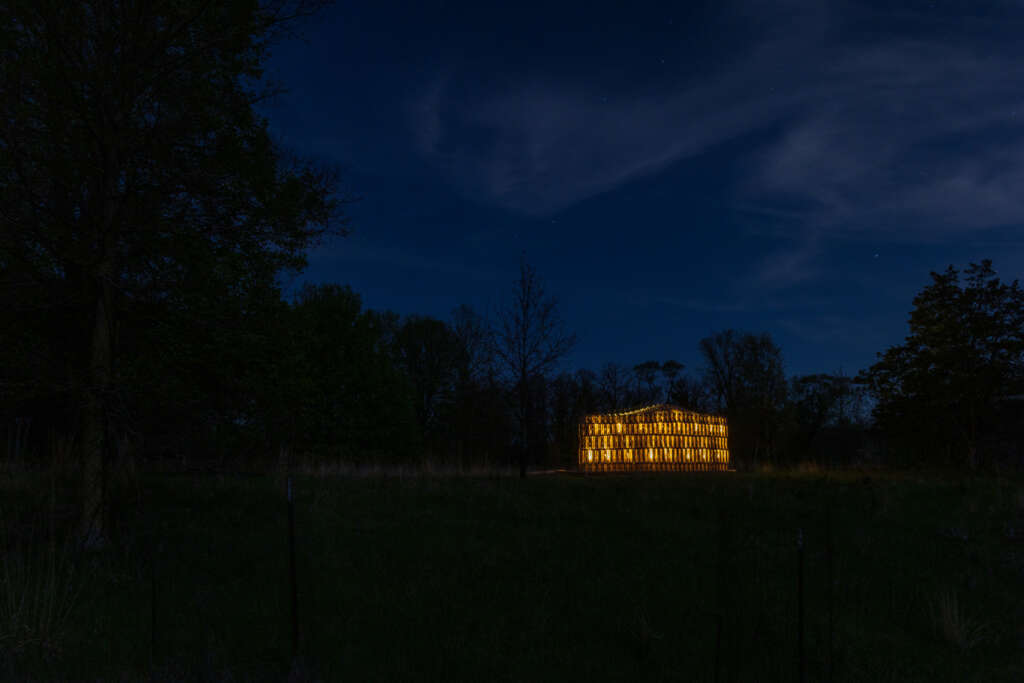
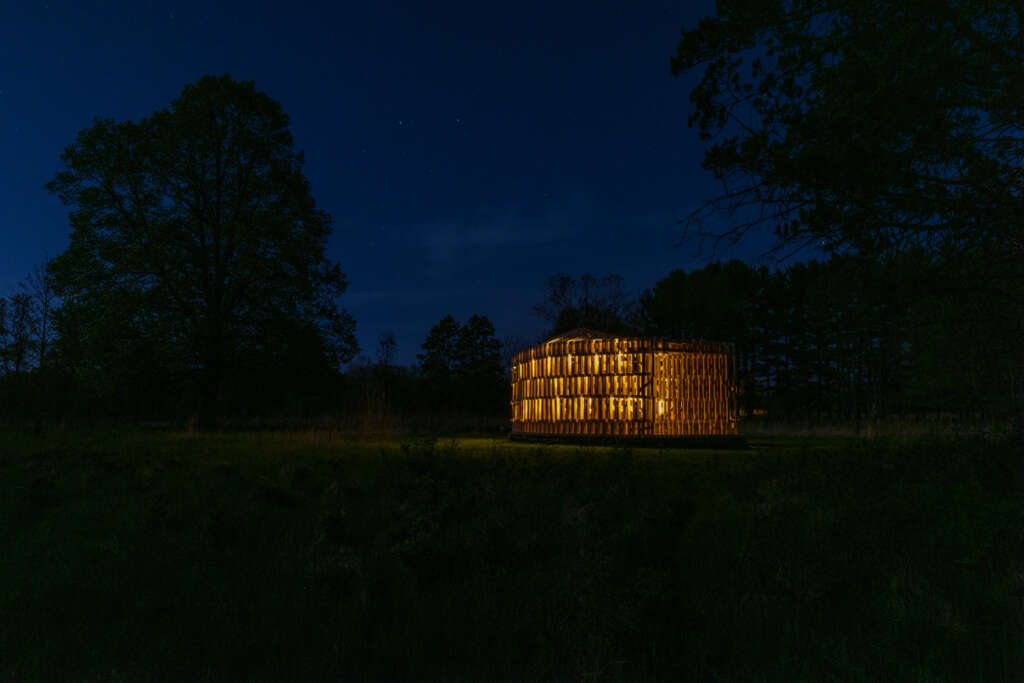
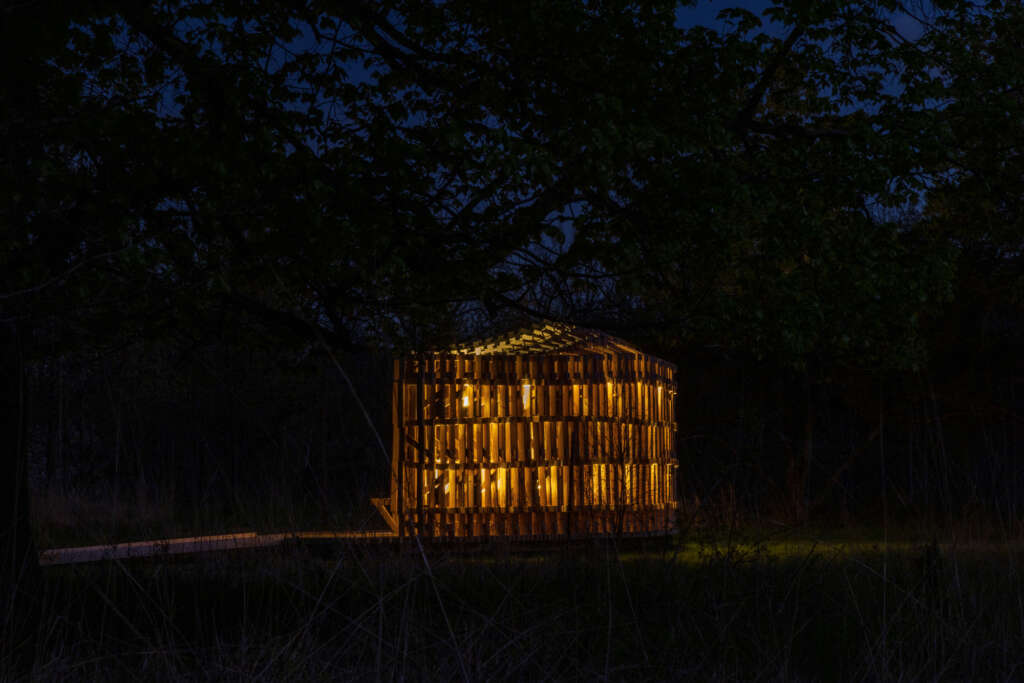




RFS is designed and fabricated by ADR Laboratory, research assistants, and students of the University of Michigan’s Taubman College MS in Digital and Material Technologies program. The work is evaluated for structural performance and building code requirements in partnership with the structural engineering firm Silman.
Project Credits
- Principal Investigator and Project Lead: Prof. Arash Adel, ADR Laboratory
- Research, Design, and Fabrication Assistants: Ben Lawson, Ryan Craney, Sarah Nail, Gabrielle Clune, Andrew Hoover, Juliette Zidek
- Construction Assistants: Abdallah Kamhawi, Tharanesh Varadharajan, Ali Fahmy, Elliot Smithberger, Qian Li, Nadim Hajj Ahmad, Joshua Powell, Ivan Gort-Cabeza de Vaca
- Students (MS in Digital and Material Technologies, Taubman College of Architecture and Urban Planning): Ruxin Xie, Daniel Ruan, Xinran Li, Jingwen Song, Mehdi Shirvani, Mackenzie Bruce, Chris Humphrey
- Structural Engineers: Robert Silman Associates Structural Engineers (Nat Oppenheimer, Omid Oliyan, Justin Den Herder, Paul Evans)
- Video Editors: Yunyan Li, Jacob Cofer
- Videographers: Jacob Cofer, Bob Berg
- Diagrams: Yunyan Li
Supported by the Herbert W. and Susan L. Johe Fund, Taubman College of Architecture and Urban Planning, University of Michigan
- Special Thanks: Prof. Jonathan Massey, Prof. McLain Clutter, Prof. Catie Newell, Prof. Wes McGee, Cynthia Radecki, Earl Bell




